Git && Github
March 18, 2020
What is Git?
Git is a version control system that tracks the changes you make to files. This allows you to have a record of what had been done, revert to specific versions, and most importantly, it allows easy collaboration from people all around the world.
Git runs locally and you can utilize it by accessing it in your terminal. The files and their history are stored locally. But you might be wondering, “if everything is saved locally, what’s the big deal?”
GitHub (or GitLab, or Bitbucket, etc)
GitHub is an online host that runs on Git that allows you to store a copy of your files remotely. This magic is what allows collaboration, easy open-source contributions, and what makes Git such a necessary tool for a developer. The easiest way to understand how these online hosts work is to imagine a Google doc that is being worked on by multiple group members. Each person is working on their own machine, but connecting to a centralized version that takes in every person’s contribution.
How it works, and some commands to become familiar with
To begin, you need to initialize a Git repository. To create this, you’ll use the git init command inside your terminal to create a new repo. This will create a new .git subdirectory and master branch for your project. You can also clone into a repository if you are wanting to collaborate with the git clone <repo url> command inside your terminal.
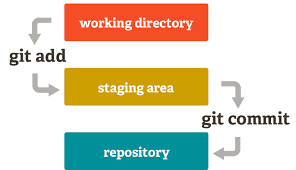
As you work on your project, you’ll use the git add && git commit -m"Your message here" to add your changes to the master file.
To commit your changes to a remote repository, such as GitHub, simply git push after running the git add and git commit commands.
And that’s the basic to getting started with Git! There is a ton more you can learn. Becoming comfortable with Git isn’t something that just gives you a leg up, but it’s something required if you are serious about becoming a developer.